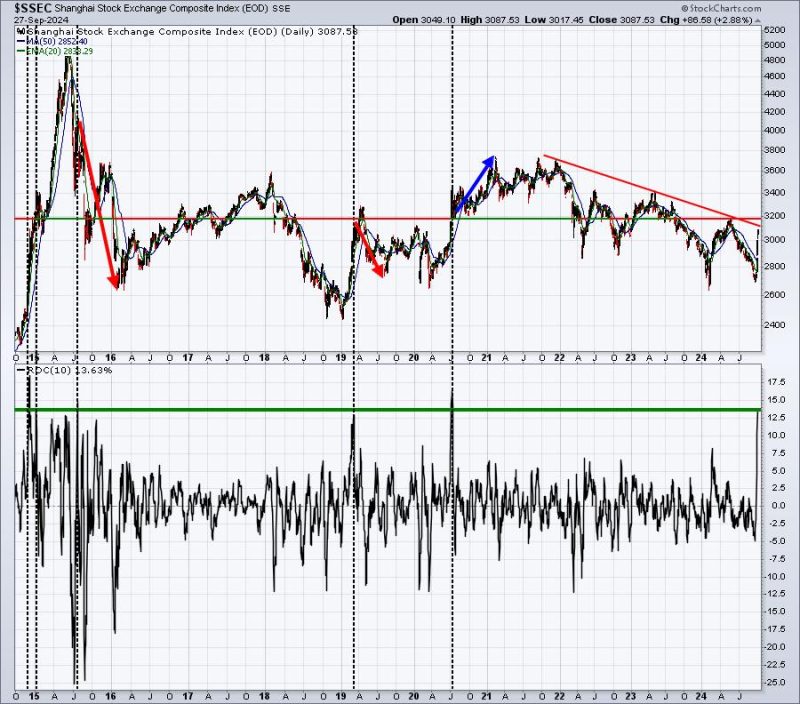
The recent surge in China’s stock market performance has taken many investors by surprise. After a tumultuous period earlier in the year due to the global economic slowdown, China’s strength seems to have made a striking comeback in the past week. The question on everyone’s mind now is whether this newfound momentum can be sustained in the long run.
One of the key factors that have contributed to China’s recent strength is its strong economic data. China’s GDP rebounded at a record pace in the second quarter of this year, indicating a faster-than-expected recovery from the pandemic-induced slump. This rapid growth has been supported by aggressive stimulus measures and robust domestic consumption, which have in turn boosted investor confidence in the Chinese market.
Another factor that has bolstered China’s stock market performance is the country’s successful containment of the Covid-19 virus. China’s swift response to the pandemic, including strict lockdown measures and mass testing, has helped the country to control the spread of the virus and minimize its impact on the economy. This has instilled confidence in investors that China is well-equipped to handle future outbreaks and minimize disruptions to economic activities.
Furthermore, China’s ongoing efforts to shift towards a more consumption-driven economy have also played a role in its recent strength. The Chinese government has been implementing policies to boost domestic consumption and reduce reliance on exports, which has helped to drive growth in sectors such as retail, e-commerce, and services. This shift in focus has diversified China’s economic base and reduced its exposure to external risks, making it a more attractive investment destination.
However, despite these positive indicators, there are still risks that could derail China’s momentum in the coming weeks and months. One of the key concerns is the ongoing geopolitical tensions between China and the United States, which have escalated in recent months due to issues such as trade, technology, and human rights. These tensions could lead to increased market volatility and undermine investor confidence in the Chinese market.
In addition, China’s high debt levels and overheated property market remain significant challenges that could weigh on the country’s economic prospects in the long run. The Chinese government has been taking steps to address these issues, such as implementing stricter lending regulations and curbing speculative real estate investments. However, the effectiveness of these measures in stabilizing the economy remains to be seen.
In conclusion, while China’s recent strength in the stock market is impressive, it is important for investors to exercise caution and carefully assess the risks before making investment decisions. The sustainability of China’s economic recovery will depend on a variety of factors, including the country’s ability to manage geopolitical tensions, control debt levels, and stimulate domestic consumption. By staying informed and monitoring developments closely, investors can navigate the opportunities and challenges presented by China’s evolving market dynamics.