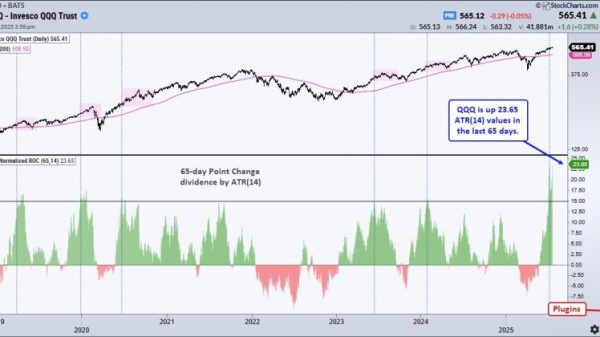
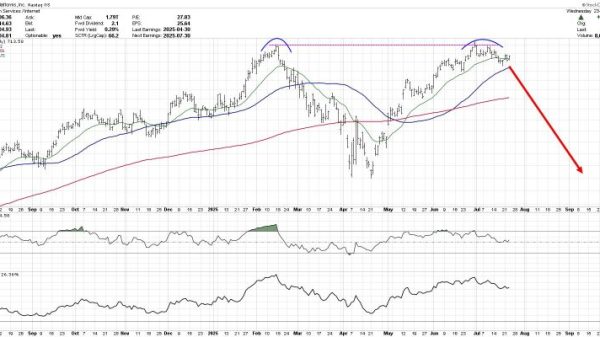
Markets are Counting on the Fed to Head off Recession with Sizable Interest Rate Cuts
As the global economy continues to face uncertain times, investors and policymakers are closely watching the actions of central banks like the Federal Reserve. The recent fears of an impending recession have led to growing expectations that the Fed will step in with significant interest rate cuts to stimulate economic growth and prevent a downturn.
One of the main tools at the disposal of central banks in managing economic cycles is the manipulation of interest rates. By lowering interest rates, central banks aim to encourage borrowing and spending, which can boost economic activity. Conversely, raising interest rates can help cool down an overheating economy to prevent inflation from spiraling out of control.
In the United States, the Federal Reserve plays a crucial role in setting interest rates and implementing monetary policy. The Fed’s decisions have far-reaching implications for the economy, influencing everything from consumer spending to business investments and market sentiment.
With the recent inversion of the yield curve—a reliable indicator of past recessions—investors and analysts are bracing for the possibility of an economic downturn. Many believe that the Fed must act decisively to prevent a recession and keep the economy on a stable growth path.
The expectation of sizable interest rate cuts from the Fed is driven by concerns over slowing global growth, trade tensions, and geopolitical uncertainties. Lowering interest rates can help ease financial conditions, support asset prices, and provide a boost to businesses and consumers.
However, there are also risks associated with an aggressive approach to interest rate cuts. Some economists caution that cutting rates too rapidly or by too much could fuel asset bubbles, distort market signals, and limit the Fed’s ability to respond effectively to future economic challenges.
Moreover, the effectiveness of interest rate cuts in stimulating economic growth is not guaranteed, especially in an environment of heightened uncertainty and structural issues. While lower interest rates can provide a short-term boost to the economy, they may not address deeper-rooted concerns such as sluggish productivity growth, income inequality, or the impact of global trade dynamics.
As the debate around interest rates and the Fed’s role in managing the economy continues, policymakers are facing a delicate balancing act. Striking the right balance between supporting growth and guarding against risks requires careful consideration of various factors, including economic data, market conditions, and long-term sustainability.
Ultimately, the markets are closely watching the Fed’s next moves, hoping that proactive measures will help avert a recession and instill confidence in the economy. While interest rate cuts can provide temporary relief, addressing the underlying challenges facing the economy may require broader policy initiatives and structural reforms to ensure sustainable and inclusive growth in the long run.